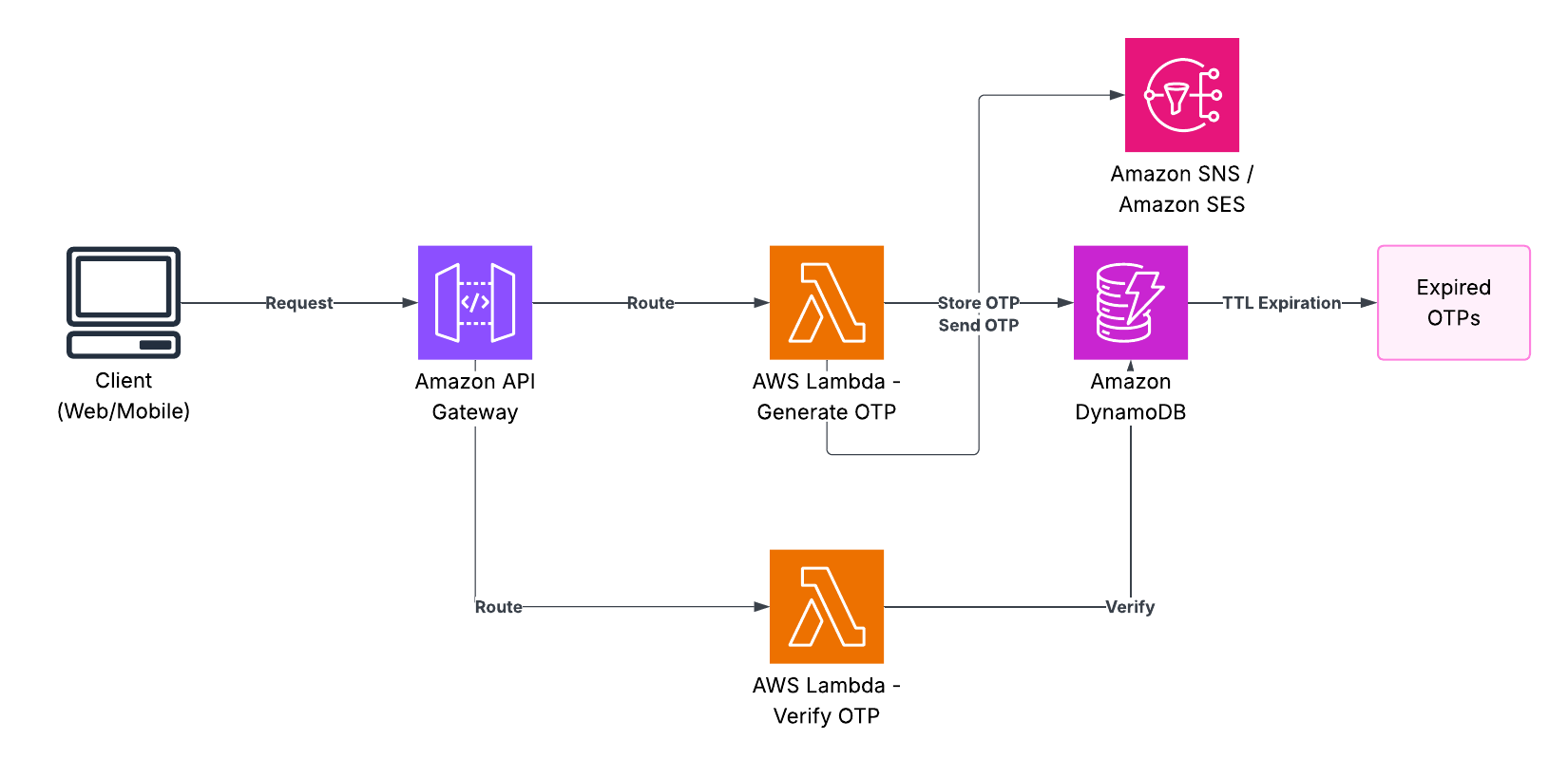
We will develop a serverless One-Time Password (OTP) system on AWS and we will code the entire set-up using Terraform. It is simply configured: we send a code in SMS with the help of Amazon SNS, and we check it with the record in DynamoDB.
A Quick Look at Serverless
Firstly, we should understand the reason of doing the serverless way before we dive into the code.
Serverless does not imply the absence of servers, as the name implies. It simply means that you do not have to contend with them. AWS manages the equipment, revision and capacity planning. You just write the code.
Why it works for us:
- No Ops: You do not need to patch an OS and deal with fleets of EC2 instances.
- Auto-Scaling: You can have five or five thousand users, and AWS balances automatically.
- Cost: This is the biggest win. You only get billed when the code is running. In case there is no one requesting an OTP then you have no bill.
Why Lambda is the Right Fit
The AWS Lambda is ideal in an OTP service due to traffic dynamics. OTP requests are sporadic typically, you may receive a bunch of them at 9:00 AM and none at 3:00 AM.
And by the time you rented a traditional server, you would be renting it to just sit there 90 percent of the time. In the case of Lambda, the function is initiated when a request is sent to the API, executes the logic in some milliseconds and terminates. You will be charged that one-second of compute time. It also works well with API Gateway and DynamoDB which are out-of-the-box compatible and hence there is less glue code to be written.
The Stack
The following are the particular pieces we are using:
- API Gateway: The front door. It provides us with our
/send-otpand/verify-otp. - AWS Lambda: The brain. It executes the logic to produce the numbers and test them.
- Amazon DynamoDB: The memory. Here we save the OTP with Time to Live (TTL) such that it will automatically expire after several minutes.
- Amazon SNS: The shipping service. This really transmits the SMS to the user.
- Terraform: The blueprint. We are using this to create the entire environment to not have to be clicking over the AWS console manually.
How the Request Flows
To picture the way this works in practice:
Send OTP Flow
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ Client │───1───▶│ API Gateway │───2───▶│ Lambda │───3───▶│ DynamoDB │ │ SNS │
│ (User) │ │ /send-otp │ │ send_otp │ │ (Store) │ │ (SMS) │
└──────────┘ └──────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └──────────┘ └─────────┘
▲ │ │
│ └──────────────4──────────────────────────┘
│ │
└──────────────────────────5: Success Response◀─────────────────────────────────────────┘
Flow Steps:
1. User sends POST request with phone number to /send-otp
2. API Gateway triggers send_otp Lambda function
3. Lambda generates 6-digit OTP and stores in DynamoDB with 5-min TTL
4. Lambda sends OTP via SNS to user's phone number
5. Success response returned to clientVerify OTP Flow
┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ Client │───1───▶│ API Gateway │───2───▶│ Lambda │───3───▶│ DynamoDB │
│ (User) │ │ /verify-otp │ │ verify_otp │ │ (Read) │
└──────────┘ └──────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └──────────┘
▲ │ │
│ └──────4───────────────┘
│ │
│ [Validation]
│ • OTP exists?
│ • Not expired?
│ • Matches input?
│ │
└──────────5: Verified True/False◀─────────────┘
Flow Steps:
1. User sends POST request with phone number and OTP to /verify-otp
2. API Gateway triggers verify_otp Lambda function
3. Lambda retrieves stored OTP from DynamoDB by userId
4. Lambda validates: existence, expiration time, OTP match
5. Response indicates verification success or specific failure reasonComponent Interaction Details
This section is a description of the interactions among the components that form the entire system.
- API Gateway: This is the access point which processes the termination of HTTPS, routing of requests, and throttling.
- Lambda Functions: Stateless execution environment which is scaled automatically with incoming requests.
- DynamoDB: Non-relational database that has automatic TTL deletion of expired OTPs which maintains a constant latency of single digits of milliseconds.
- SNS: Trusted SMS delivery platform that covers 200 plus countries with inbuilt retries.
- IAM Roles: Least-privilege access which guarantees that Lambda can access only what is necessary.
Prerequisites
- AWS Account
- Terraform installed (>= 1.0.0)
- AWS CLI configured
- Basic knowledge of AWS services and Python
Project Structure
Your project should be organized as follows:
.
├── main.tf
├── variables.tf
├── outputs.tf
├── lambda/
│ ├── send_otp.py
│ └── verify_otp.py
└── lambda.zip (Generated from lambda/ directory)Step-by-Step Implementation
Accessing AWS Lambda from the AWS Management Console - Search for "Lambda" in the services search bar to navigate to the Lambda dashboard where you can create and manage your functions.
Step 1: Write Lambda Functions
Write the Python scripts of your Lambda functions in the directory called lambda.
The OTP service is based on our Lambda functions as the main business logic. The send_otp.py application obtains a 6-digit OTP by generating a number randomly and storing it in DynamoDB with an expiry date and transmitting it through SMS. The verify_otp.py feature authenticates the OTPs entered by users and compares them with the stored OTPs and verifies expiration.
lambda/send_otp.py
Description of the Function: This is the OTP generation and delivery function. It is fed a phone number, creates a random OTP, which is secure, and with a TTL (Time To Live) of 5 minutes, it is placed in DynamoDB and sent through Amazon SNS. The role will cover all aspects of error management related to JSON parsing, parameter omissions, and service errors of the Amazon.
import json
import boto3
import random
import time
import os
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
sns = boto3.client('sns')
# Ensure OTP_TABLE environment variable is set in Lambda configuration
table_name = os.environ.get('OTP_TABLE')
if not table_name:
raise ValueError("Missing OTP_TABLE environment variable")
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
try:
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
except json.JSONDecodeError:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Invalid JSON in request body'})
}
user_id = body.get('userId') # Phone number for SMS
if not user_id:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'userId (phone number) is required'})
}
otp = str(random.randint(100000, 999999))
# TTL for 5 minutes (300 seconds)
# DynamoDB TTL attribute must be a Unix epoch timestamp in seconds
ttl_timestamp = int(time.time()) + 300
try:
table.put_item(Item={
'userId': user_id,
'otp': otp,
'expirationTime': ttl_timestamp # Ensure this matches TTL attribute in DynamoDB
})
sns.publish(
PhoneNumber=user_id,
Message=f"Your OTP is: {otp}"
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing OTP: {e}") # Log error for debugging
return {
'statusCode': 500,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Failed to send OTP', 'details': str(e)})
}
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'message': 'OTP sent successfully'})
}
lambda/verify_otp.py
Function Overview: This is a validation OTP submission. It retrieves the stored OTP in DynamoDB as assistance of the userId, whether it has not expired and compares the given OTP by the user and gives the appropriate success / failure notification. The function uses appropriate codes of the status of an HTTP (404-not found, 410- expired, 401- invalid) to give information on the different situations of failures.
import json
import boto3
import time
import os
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
# Ensure OTP_TABLE environment variable is set in Lambda configuration
table_name = os.environ.get('OTP_TABLE')
if not table_name:
raise ValueError("Missing OTP_TABLE environment variable")
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
try:
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
except json.JSONDecodeError:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'Invalid JSON in request body'})
}
user_id = body.get('userId')
input_otp = body.get('otp')
if not user_id or not input_otp:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'userId and otp are required'})
}
try:
response = table.get_item(Key={'userId': user_id})
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error fetching OTP from DynamoDB: {e}")
return {
'statusCode': 500,
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'Failed to retrieve OTP details', 'details': str(e)})
}
item = response.get('Item')
if not item:
return {
'statusCode': 404,
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'OTP not found or already used'})
}
# Check if OTP has expired - DynamoDB TTL should handle deletion,
# but this is a good safeguard if item hasn't been reaped yet.
# 'expirationTime' is expected to be a Unix epoch timestamp in seconds.
if int(time.time()) > item.get('expirationTime', 0):
# Optionally, delete the expired item here if not relying solely on TTL
# table.delete_item(Key={'userId': user_id})
return {
'statusCode': 410, # HTTP 410 Gone
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'OTP expired'})
}
if item.get('otp') == input_otp:
# Optionally, delete the OTP item after successful verification
# to prevent reuse, if not relying on TTL for cleanup.
# table.delete_item(Key={'userId': user_id})
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'verified': True, 'message': 'OTP verified successfully'})
}
return {
'statusCode': 401, # HTTP 401 Unauthorized
'body': json.dumps({'verified': False, 'error': 'Invalid OTP'})
}
Lambda functions deployed in AWS Console - The Code tab shows both send_otp.py and verify_otp.py files in the Lambda function editor, confirming successful deployment of our OTP service functions.
Step 2: Terraform Configuration
Prepare the following Terraform files in the top of your project.
Using Terraform we can just code our complete infrastructure and it can be reproducible, auditable and versioned. The configuration gives everything that AWS needs like DynamoDB tables, lambda functions, least-privileged IAM roles, API Gateway endpoints, and the necessary inter-service connections.
main.tf
This file is used to configure all the AWS resources like the IAM roles and permissions that are needed. Note the way in which we are using random name to generate resource names and they would not conflict with each other in the event you are deploying more than one environment. The IAM policies have been founded on the principle of least privilege, the principle entails the granting of a given set of permissions as mandated by each Lambda function.
provider "aws" {
region = var.aws_region
}
# --- DynamoDB Table for OTPs ---
resource "aws_dynamodb_table" "otp_table" {
name = "OTPsTable-${random_id.suffix.hex}" # Unique table name
billing_mode = "PAY_PER_REQUEST"
hash_key = "userId" # Primary key
attribute {
name = "userId" # Phone number or user identifier
type = "S" # String
}
# TTL (Time To Live) configuration to automatically delete expired OTPs
ttl {
attribute_name = "expirationTime" # Must match the attribute name in Lambda
enabled = true
}
tags = {
Name = "OTPStorageTable"
Environment = "Production" # Or your environment
}
}
# Generate a random suffix for unique resource naming
resource "random_id" "suffix" {
byte_length = 4
}
# --- IAM Role and Policies for Lambda ---
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_exec_role" {
name = "otp_lambda_exec_role-${random_id.suffix.hex}"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole",
Effect = "Allow",
Principal = { Service = "lambda.amazonaws.com" }
}]
})
tags = {
Name = "OTP Lambda Execution Role"
}
}
# Basic Lambda execution policy (CloudWatch Logs)
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "lambda_basic_exec_policy" {
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_exec_role.name
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole"
}
# Custom IAM policy for DynamoDB and SNS access
resource "aws_iam_policy" "lambda_custom_permissions_policy" {
name = "otp_lambda_permissions_policy-${random_id.suffix.hex}"
description = "Policy for Lambda to access DynamoDB OTP table and publish to SNS"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = [
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:DeleteItem", # If you implement OTP deletion after verification
"dynamodb:UpdateItem" # If you need to update items
],
Resource = aws_dynamodb_table.otp_table.arn
},
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = ["sns:Publish"],
Resource = "*" # Restrict this to specific SNS topics in production if possible
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "lambda_custom_permissions_attachment" {
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_exec_role.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.lambda_custom_permissions_policy.arn
}
# --- Lambda Functions ---
# Package the lambda functions
data "archive_file" "lambda_zip" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = "${path.module}/lambda/"
output_path = "${path.module}/lambda.zip"
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "send_otp_lambda" {
filename = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_path
function_name = "sendOTPFunction-${random_id.suffix.hex}"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_exec_role.arn
handler = "send_otp.lambda_handler" # Corresponds to filename.function_name
runtime = "python3.12"
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
OTP_TABLE = aws_dynamodb_table.otp_table.name
}
}
tags = {
Name = "SendOTP Lambda"
}
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "verify_otp_lambda" {
filename = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_path
function_name = "verifyOTPFunction-${random_id.suffix.hex}"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_exec_role.arn
handler = "verify_otp.lambda_handler" # Corresponds to filename.function_name
runtime = "python3.12"
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
OTP_TABLE = aws_dynamodb_table.otp_table.name
}
}
tags = {
Name = "VerifyOTP Lambda"
}
}
# --- API Gateway (HTTP API v2) ---
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_api" "otp_api" {
name = "OTPApi-${random_id.suffix.hex}"
protocol_type = "HTTP"
description = "API Gateway for Serverless OTP Service"
tags = {
Name = "OTP Service API"
}
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_stage" "default_stage" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.id
name = "$default" # Default stage
auto_deploy = true # Automatically deploy changes
tags = {
Name = "OTP API Default Stage"
}
}
# API Gateway Integrations with Lambda
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "send_otp_integration" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.id
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY" # For Lambda proxy integration
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.send_otp_lambda.invoke_arn
payload_format_version = "2.0" # For HTTP APIs
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "verify_otp_integration" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.id
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY"
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.verify_otp_lambda.invoke_arn
payload_format_version = "2.0"
}
# API Gateway Routes
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_route" "send_otp_route" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.id
route_key = "POST /send-otp" # Method and path
target = "integrations/${aws_apigatewayv2_integration.send_otp_integration.id}"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_route" "verify_otp_route" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.id
route_key = "POST /verify-otp"
target = "integrations/${aws_apigatewayv2_integration.verify_otp_integration.id}"
}
# Permissions for API Gateway to invoke Lambda functions
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "api_gw_send_otp_permission" {
statement_id = "AllowAPIGatewayInvokeSendOTP"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.send_otp_lambda.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
# Source ARN restricts which API Gateway can invoke this Lambda
source_arn = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "api_gw_verify_otp_permission" {
statement_id = "AllowAPIGatewayInvokeVerifyOTP"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.verify_otp_lambda.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
variables.tf
variable "aws_region" {
description = "The AWS region to deploy resources into."
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
outputs.tf
output "api_endpoint" {
description = "The base URL endpoint for the OTP API."
value = aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.api_endpoint
}
output "send_otp_endpoint" {
description = "Full URL to the /send-otp endpoint."
value = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.api_endpoint}/send-otp"
}
output "verify_otp_endpoint" {
description = "Full URL to the /verify-otp endpoint."
value = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.otp_api.api_endpoint}/verify-otp"
}
output "otp_table_name" {
description = "Name of the DynamoDB table used for storing OTPs."
value = aws_dynamodb_table.otp_table.name
}
Step 3: Deploy the Stack
Make sure that your Lambda code of operation is found in the lambda folder before deploying. Terraform configuration is able to zip this directory automatically using an archive file, data.
-
Initialize Terraform:
Enter this command in the first level of your project (initial directory with your
.tffiles):terraform init -
Plan the deployment:
This will demonstrate what will be created by Terraform.
terraform plan -
Introduction of Terraform configuration:
This will provision the AWS account of resources. Certify by answering yes by typing it on the screen.
terraform apply
Upon deployment, Terraform will provide the URLs of the endpoints of the API. You are now able to make POSTs to:
https://.execute-api. .amazonaws.com/send-otp
Request Body:{ "userId": "+11234567890" }(organize E.164 formatted phone number)https://.execute-api. .amazonaws.com/verify-otp
Request Body:{ "userId": "+11234567890", "otp": "123456" }
In order to clean up and destroy all created resources, do:
terraform destroyTesting and Validation
Ensuring your OTP service is later tested properly before production deployment entails that you take this test into consideration. The following are some of the methods of testing your endpoints:
Using cURL (Command Line)
Upon the execution of the Terraform, the output format will contain API endpoint URLs. Test using cURL, using the following URLs:
Send OTP Request
curl -X POST https://your-api-id.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/send-otp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"userId": "+11234567890"}'Expected Response:
{"message": "OTP sent successfully"}You will be expected to get an SMS containing the 6-digit OTP in the given phone number.
Verify OTP Request
curl -X POST https://your-api-id.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/verify-otp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"userId": "+11234567890", "otp": "123456"}'Expected Response (Valid OTP):
{"verified": true, "message": "OTP verified successfully"}Expected Response (Invalid OTP):
{"verified": false, "error": "Invalid OTP"}Using Postman (GUI Tool)
Postman is also simpler to interface:
- Insert a new POST message in Postman.
- Replace the URL with an otp endpoint of the same.
- On the tab of the body, select the option of raw and format of the data to be in the JSON format.
- Make POST request:
{"userId": "+11234567890"} - Press the button send and have the response.
- Similarly, we should do the same with
/verify-otpendpoint with received OTP.
Testing Edge Cases
General test on various situations should be carried out:
- Un-Valid Phone number format: This is a test of incorrect phone numbers in order to determine the warning messages.
- Expired OTP: Wait 5 minutes after an OTP has been generated and verify (this must fail with the error of OTP expired)
- Missing Parameters: Check the error handling, submit requests with missing parameters.
- Bad JSON: This is used to test the error responses in parsing by running bad JSON.
- Non-Existent User: Trying to check OTP of a userId which does not request OTP non-existent user.
Best Practices and Error Handling
Error handling, performance optimization and security have to be taken into consideration carefully when building production-ready serverless applications. These are some of the key considerations:
End to end Error Management
Patterns of Lambda Functions Mistakes
We are implementing many levels of error management:
- Input Checking: Incoming information must always be checked before its processing. Check on the presence of required fields, right data types and the expected formats (e.g., E.164 phone format).
- Try-Catch Blocks: AWS service calls should be surrounded by exception handlers to handle network problems, access control errors or access control throttling.
- Educational Error Messages: Provide meaningful error messages that can be used to diagnose the problem without disclosing confidential system information.
- Proper HTTP Status codes: HTTP semantic status codes (400 in the case of bad requests, 401 in the case of authentication failures, 404 not found, 500 server errors).
Retry Logic and Idempotency
Add mechanism of retries in case of transient failures:
- Exponential Backoff: Backoff-At least when retries are applied to failed operations, exponential downplaying is used to prevent overloading downstream services.
- Idempotence Operations: Design is regarded to be the same as when calling functions with inputs which then result in the same outcome without any undesired side effects. In the service of OTP, you can consider relating a timestamp or request id to avoid duplicate transmission of SMS.
- Dead Letter Queues (DLQ): Enable Lambda DLQs to receive gained events, which can be analysed or reprocessed.
Managing Cold Starts
The cold starts are observed when Lambda creates a fresh execution environment, which delays returns more on the first call. The mitigation measures are:
- Warm aviation: Warm Lambda instances Warm Lambda instances, provide predictable performance by configuring provisioned concurrency (note: more expensive).
- Minimize the Size of the Package: Minimize the size of the deployment package by eliminating unnecessary dependency. Smaller packages minimize the time of initiating.
- Code Optimization: Extraction: Extract Initialize Keeps uninitiating code outside the handler function to execute it on a per-container-family basis as opposed to a per-invocation-family basis.
- Connection Pooling: Recycle database and AWS SDK clients between calls by declaring them outside the handler.
- Select Suitable Memory: Increased memory allocation leaves more CPU, capable of cutting on start-up time.
Example of optimized Lambda structure:
# Initialize clients outside handler (runs once per container)
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
sns = boto3.client('sns')
table = dynamodb.Table(os.environ['OTP_TABLE'])
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Handler logic here - reuses initialized clientsSecurity Best Practices
IAM Policies- Least Privilege Principle
Provide access to a minimum number of permissions:
- Resource-Specific Policies resource-specific policies: The Terraform configuration leaves DynamoDB access on all tables, but only to OTP table ARN.
- Action-Specific Permissions: This should have action-specific permissions, e.g. only what is necessary (GetItem, PutItem) as opposed to sets of wildcards such as
dynamodb:*. - SNS Restrictions: Limit SNS publish to particular topics or exchange number patterns rather than
Resource: "*".
API Security
Improve the API Gateway insecurity:
- API keys: API keys are also required on each request to ensure that it is not accessed without authorization.
- Usage Plans and Throttling: Set rate limits to avoid abuse (e.g. 10 requests per minute per user).
- AWS WAF Integration: Instance AWS Web Application Firewall to mitigate most common attacks (SQL injection or DDoS).
- Request Validation: API Gateway request validation to deny the malformed requests to Lambda.
- CORS Set up: In case of a web front, set up CORS appropriately to just allow trusted domains.
Data Protection
- Encryption at Rest: DynamoDB encryption is a feature that encrypts any stored OTPs (keys are managed automatically by AWS).
- Encryption in Transit: API Gateway is by default configured to use HTTPS, which means that the data is encrypted on the way.
- Short TTL Values: OTP expiration times should be as short as possible (less than 5 minutes) to reduce exposure times.
- Generation of OTP Cryptographically Secure: Use of Cryptographically secure random number generators. The
random.SystemRandom()of Python is more production-safe thanrandom.randint()is.
Logging and Debugging
CloudWatch Integration
The logs are automatically transferred to CloudWatch by the Lambda. Improve observability using the following practices:
- Structured Logging: Use of JSON structure to enable easy parsing and querying of the log events.
- Contextual Information: Log entries should contain request identifiers, user identifiers, and time to correlate them.
- Log Levels: It is advisable to use the right levels ( INFO, warning, error) to filter logs.
- Avoid Logging Sensitive Data: OTPs and phone numbers should never be logged in any production.
Example structured logging:
import json
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
logger.info(json.dumps({
'event': 'otp_generation',
'request_id': context.request_id,
'status': 'started'
}))AWS X-Ray distributed tracing
Trace service requests in AWS X-Ray:
- end-to-end-visibility: Monitor API Gateway to Lambda to DynamoDB and SNS requests.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Fast operations- identify the slowness and optimize them.
- Error Analysis: Visualize request chain errors.
Enables X-Ray in Terraform: Add to Lambda configuration:
tracing_config {
mode = "Active"
}Cost Optimization
- Right-Size Memory: Lambda memory influences prices. You can start with 128MB and upgrade depending on the performance tests.
- Monitor Invocations: CloudWatch metrics can be used to monitor invocation counts and detect unusual spikes of usage.
- DynamoDB On-Demand vs Provisioned: In unpredictable workloads, an on-demand pricing (which we have implemented) may be cheaper.
- SNS Cost Management: The cost of SMS differs by the country. Tracking SNS costs and rate limiting to eliminate abuse.
- Create Budget Scripts: Enabling AWS Budgets to notify you when your spending is beyond certain limits.
Production Checklist Ready Checklist
Before going to production, make sure that you have tackled:
- ✓ Installed error recovery and retries.
- ✓ Error and throttling CloudWatch alarm configuration.
- ✓ Encleaned AWS X-Ray distributed tracing.
- ✓ Applied least-privilege IAM is using the least-privilege policies.
- ✓ Install API rate limiting and throttling.
- ✓ Point-in-Time DynamoDB Disaster recovery.
- ✓ Lambda Scale: Reserved concurrency was on enabled Lamps to avoid runaway costs.
- ✓ Tested every possible error (expired OTPs, broken inputs, network errors).
- ✓ Install surveillance boards and notifications.
- ✓ Published API endpoints and error codes.
- ✓ Carried out load testing in order to test the behavior of auto-scaling.
Security Concerns and Sophisticated Best Practices
A production OTP service development demands to handle essential security and cost issues that will pose a major challenge to the reliability and cost of your application.
SMS Cost Management and Prevention
The charges charged through the Amazon SNS in terms of delivering SMS depend strongly on the destination country. Unless there are proper controls, it is possible to incur unexpected costs due to malicious actors or bugs.
SMS Pricing Reality Check
- United States: $0.00645 cents/SMS (quite cheap)
- India: $0.00425 per SMS
- United Kingdom: $0.04290 /SMS (10 times higher)
- Germany: $0.07240 per SMS
- Kuwait: $0.11550 per SMS (27x US cost)
Scenario of Cost: It would be costs you $1,155 in a minute just in minutes, in case, an attacker sent 10,000 messages to the Kuwait numbers using SMS.
Implementing Rate Limiting
Install DynamoDB monitoring to avoid spamming via SMS:
import time
def lambda_handler(event, context):
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
user_id = body.get('userId')
# Check rate limit: max 3 OTPs per phone number per hour
rate_limit_key = f"rate_limit_{user_id}"
try:
response = table.get_item(Key={'userId': rate_limit_key})
item = response.get('Item')
if item:
attempts = item.get('attempts', 0)
last_reset = item.get('last_reset', 0)
current_time = int(time.time())
# Reset counter every hour
if current_time - last_reset > 3600:
attempts = 0
last_reset = current_time
if attempts >= 3:
return {
'statusCode': 429, # Too Many Requests
'body': json.dumps({
'error': 'Rate limit exceeded',
'message': 'Maximum 3 OTP requests per hour',
'retry_after': 3600 - (current_time - last_reset)
})
}
# Increment attempt counter
table.put_item(Item={
'userId': rate_limit_key,
'attempts': attempts + 1,
'last_reset': last_reset,
'expirationTime': current_time + 3600
})
else:
# First attempt
table.put_item(Item={
'userId': rate_limit_key,
'attempts': 1,
'last_reset': int(time.time()),
'expirationTime': int(time.time()) + 3600
})
except Exception as e:
print(f"Rate limiting error: {e}")
# Fail closed - deny request if rate limiting fails
return {
'statusCode': 503,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Service temporarily unavailable'})
}
# Continue with normal OTP generation
otp = str(random.randint(100000, 999999))
# ... rest of the codeGeographic SMS Restrictions
Restrict SMS delivery to approved countries to manage costs:
import phonenumbers
ALLOWED_COUNTRY_CODES = ['US', 'IN', 'CA', 'AU'] # Define allowed countries
def validate_phone_number(phone_number):
"""Validate phone number format and country"""
try:
parsed = phonenumbers.parse(phone_number, None)
if not phonenumbers.is_valid_number(parsed):
return False, "Invalid phone number"
country_code = phonenumbers.region_code_for_number(parsed)
if country_code not in ALLOWED_COUNTRY_CODES:
return False, f"SMS not supported for country: {country_code}"
return True, None
except phonenumbers.NumberParseException:
return False, "Invalid phone number format"
def lambda_handler(event, context):
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
user_id = body.get('userId')
# Validate phone number and country
is_valid, error_message = validate_phone_number(user_id)
if not is_valid:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({
'error': error_message,
'supported_countries': ALLOWED_COUNTRY_CODES
})
}
# Continue with OTP generation...Cost Monitoring Alarms
Set up CloudWatch billing alarms for SNS spending:
Resources:
SNSCostAlarm:
Type: AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm
Properties:
AlarmName: HighSNSCosts
AlarmDescription: Alert when SNS costs exceed threshold
MetricName: EstimatedCharges
Namespace: AWS/Billing
Statistic: Maximum
Period: 21600 # 6 hours
EvaluationPeriods: 1
Threshold: 50.0 # Alert at $50
ComparisonOperator: GreaterThanThreshold
Dimensions:
- Name: ServiceName
Value: AmazonSNS
AlarmActions:
- !Ref AlertSNSTopicOTP Retry Limits and Security
Implement verification attempt limits to prevent brute-force attacks:
Track Failed Verification Attempts
def lambda_handler(event, context):
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
user_id = body.get('userId')
input_otp = body.get('otp')
# Track verification attempts
attempt_key = f"verify_attempts_{user_id}"
try:
attempt_record = table.get_item(Key={'userId': attempt_key})
if attempt_record.get('Item'):
failed_attempts = attempt_record['Item'].get('failed_attempts', 0)
# Lock account after 5 failed attempts
if failed_attempts >= 5:
return {
'statusCode': 403,
'body': json.dumps({
'verified': False,
'error': 'Account temporarily locked',
'message': 'Too many failed attempts. Request new OTP in 15 minutes.'
})
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error checking attempts: {e}")
# Get stored OTP
response = table.get_item(Key={'userId': user_id})
item = response.get('Item')
if not item:
# Increment failed attempts
increment_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key)
return {
'statusCode': 404,
'body': json.dumps({
'verified': False,
'error': 'OTP not found or expired'
})
}
# Check expiration
if int(time.time()) > item.get('expirationTime', 0):
# Don't increment attempts for expired OTPs
return {
'statusCode': 410,
'body': json.dumps({
'verified': False,
'error': 'OTP expired',
'message': 'Request a new OTP'
})
}
# Verify OTP
if item.get('otp') == input_otp:
# Success - clear attempt counter and delete OTP
table.delete_item(Key={'userId': attempt_key})
table.delete_item(Key={'userId': user_id})
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
'verified': True,
'message': 'OTP verified successfully'
})
}
# Failed verification - increment counter
increment_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key)
return {
'statusCode': 401,
'body': json.dumps({
'verified': False,
'error': 'Invalid OTP',
'attempts_remaining': 5 - get_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key)
})
}
def increment_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key):
"""Increment failed verification attempts"""
try:
current_attempts = get_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key)
table.put_item(Item={
'userId': attempt_key,
'failed_attempts': current_attempts + 1,
'expirationTime': int(time.time()) + 900 # 15 min lockout
})
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error incrementing attempts: {e}")
def get_failed_attempts(user_id, attempt_key):
"""Get current failed attempt count"""
try:
response = table.get_item(Key={'userId': attempt_key})
return response.get('Item', {}).get('failed_attempts', 0)
except:
return 0Additional Security Hardening
1. OTP Complexity and Entropy
Use cryptographically secure random number generation:
import secrets
# Instead of: otp = str(random.randint(100000, 999999))
# Use:
otp = str(secrets.randbelow(900000) + 100000) # Cryptographically secure2. Phone Number Validation
Prevent attacks using invalid or premium-rate numbers:
- Validate E.164 format: +[country code][number]
- Block premium-rate prefixes
- Implement allowlist for trusted number ranges
- Verify number isn't VoIP or disposable
3. Request Origin Validation
Implement CAPTCHA or challenge tokens to prevent automated abuse:
# Verify reCAPTCHA token before sending OTP
def verify_recaptcha(token):
"""Verify Google reCAPTCHA token"""
import requests
secret_key = os.environ['RECAPTCHA_SECRET']
response = requests.post(
'https://www.google.com/recaptcha/api/siteverify',
data={
'secret': secret_key,
'response': token
}
)
result = response.json()
return result.get('success', False) and result.get('score', 0) > 0.54. Honeypot Fields
Add hidden fields to detect bot submissions:
def lambda_handler(event, context):
body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}'))
# Check honeypot field (should be empty)
if body.get('website') or body.get('url'):
# Likely bot - fail silently
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'message': 'OTP sent successfully'})
}
# Continue with normal processing...Conclusion
With Terraform, you have managed to design and deploy a scalable, serverless, and secure system of delivering OTP. This design operates through exposing the endpoints on AWS API Gateway, a business logic on AWS Lambda, an SMS sending service on Amazon SNS, and a persistent storage of OTP on auto-expiry on Amazon DynamoDB. The entire infrastructure is code managed; it is repeatable, versionable, and auditable.